
|
|
THE EVIDENCE AGAINST DARWIN'S THEORY AS AN EXPLANATION FOR THE ORIGIN OF LIFE We now know that new species can come into existence over relatively short periods of time. The green anole lizard in Florida is an example where a rapid change in body parts took place over a short period of time. The lizard is reported to have adapted in just 15 years by developing larger toepads and more scales which helped it cling to higher branches to avoid competition from a sudden invasion of brown lizards on lower branches. It has not been claimed that the new variant of green lizard can be classed as a new species of lizard but it does illustrate how rapidly species can adapt to changes in their environment. Natural Selection or survival of the fittest has resulted in those green lizards born with larger toepads and more scales surviving more succesfully than those without those traits. These traits were already present to some degree within the population at the time, and coupled with the capability for the same traits to become even more pronounced and prolific thanks to the ingenius adaptability built into the design of the genome, spurred on by survival pressures, they are now in even greater prevalence. Over the period of 15 years the numbers of those that were being born without the advantageous traits failed to survive as successfully as those that did, and produce off spring, so the population increasingly became one with the advantageous traits. Sadly the green lizard population of Florida does not sport a National Health Service where the disadvantaged are helped to survive. This is clearly not an example of Neo-Darwinism or any variant of the same involving random mutations in action over long ages. Note that this falls well short of monkeys to men evolution although it does show that natural selection is a force for change in the body parts of existing species, and noone disagrees with that. Natural selection explains the survival of species but not their arrival! VIRUSES AND EVOLUTION Viruses are not strictly speaking living organisms and need a host to occupy in order to survive and multiply. They multiply rapidly typically producing 10 million new viruses within 24 hours, so the scope for genetic differences to emerge over short periods of time is enormous. Although a virus normally damages its host by commandeering the resources within its cells to replicate it is not in the viruses best interest to kill its host. An obvious question is 'does the Darwinian Evolution mechanism come into its own where viruses are concerned?'. Viruses are obviously in a league of their own and the scope for evolutionary type processes to yield new variants over relatively brief periods of time is huge compared to the case of normal life forms. Random mutations occur at a very rapid rate, but viruses cannot be used to lend credence to the theory of evolution because this would necessitate new life forms emerging from changes to the virus over long ages. Most people would agree that once a virus always a virus, and in any case a virus is not strictly a living organism although it is still ingeniously designed and difficult to thwart, Covid 19 being a good example. Clearly the above does not illustrate Darwinian Evolution in action. The Bible refers to the creation of different 'kinds', which are a broader category than 'species'. It explaines that God created the different kinds of organisms each of which reproduced "after their kind". Creationists believe that all life on Earth today stems from the original 'created kinds', sometimes by hybridization, the process of crossing two genetically different individuals of the same kind to produce a third individual with a different, often preferred, set of traits. An example of an animal hybrid is a mule. The animal is produced by a cross between a horse and a donkey. Liger, the offspring of a tiger and a lion, is another animal hybrid. There is clearly scope here for producing a variety of new species from initial created kinds. For example, horses, donkeys and mules are entirely separate species of the same kind, and the production of mules is in no way a product of evolution. Created kinds also have enormous in-built capacity to adapt to changing environmental conditions in order to survive by, for example, making use of the vast wealth of alternative genetic information already present in the genome of every life form. Example to illustrate the point: "A 2016 paper in Nature demonstrated that the dark colour in peppered moths is not a product of random mutation. Rather, it appears that a stretch of moveable DNA (a transposon) is responsible for the colour variation. Transposons are stretches of DNA that are able to move around between various places in the genome. This allows organisms to generate variation within their "kind"; most creationists believe this is a God-designed system that permits different species to adapt to a range of environmental challenges. In this case, a certain transposon inserting itself into one particular place in the moth genome is responsible for the dark colour. Researchers found that ~95% of all black peppered moths, but none of the light-coloured variants, carried this stretch of DNA in that position. This inserted segment is large and complex, consisting of 21,925 DNA letters. So it appears that the expression of the dark trait is due to a complex and well-designed section of code, not a simple, random mutation." Transposons explain how the rich variety of life forms we see today were able to be produced over time thanks to the ingenius design of the initial created kinds. This process is quite distinct from Darwins naturalistic, God denying, explanation for the origin of life which has never been able to account for how life first emerged in the absence of a designer. Such changes can of necessity occur virtually overnight whereas Darwin's blind and unguided mechanism involving random mutations and natural selection is likely according to its advocates to take millions, if not billions, of years to yield substantive results of the kind that have led to the rich variety of life forms we see on Earth today. Genes (DNA sequences defining proteins for example) can be automatically switched on and off using genetic switches under the right environmental conditions. Evidence so far suggests that changes in gene regulation (turning genes on and off) may contribute to the origin of new species. Gene regulation is accomplished by a variety of mechanisms including chemically modifying genes and using regulatory proteins to turn genes on or off, all accomplished automatically on demand within the cell. We are only just beginning to scratch the surface of the understanding of what goes on inside living cells. Another mechanism for the possible emergence of new species is where an ancestral population splits into two or more genetically distinct descendant populations. This results in reproductive isolation of groups within the original population and accumulation of genetic differences between the two groups due to inevitable genetic changes (MUTATIONS) over time. Significant differences may develop over time to warrant classifying the 2 populations as distinct species (a species is a group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring, so if 2 such populations are unable or unwilling to breed with one another they can be classed as separate species). The factors that determine the duration of time needed will depend on such things as breeding rates, life span of the organism, etc. Example to illustrate how organisms, in this case a plant, can adapt to improve their chance of survival using existing genetic material, courtesy of God. "The Lure of a fake fly ups a daisy's pollen count", (Daily Telegraph, 24/3/23) by Science Editor Sarah Knapton: 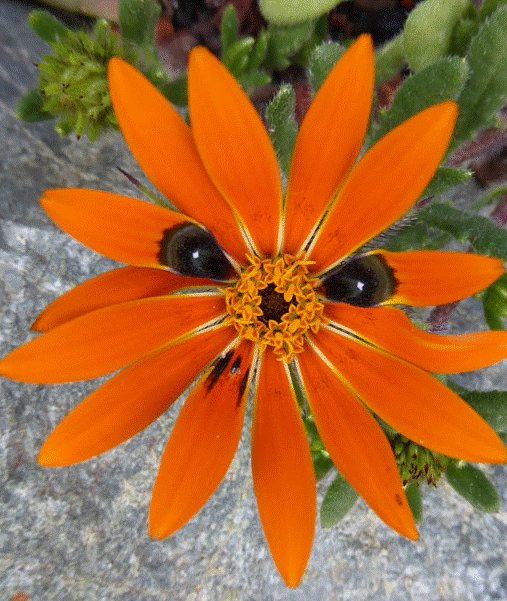
Is David Attenborough an atheist or an agnostic?
Video where the great David Attenborough explains his views about God
Age of Earth considerations
For your amusement and light relief
Convincing evidence for Design from Evolution News
|

